Choosing the best mining conveyor system means you need to look at your mining needs. You will face problems like material falling off, belts slipping, rough wear, bad transfer spots, and matching issues. These problems can make machines stop working and cost more money. When picking a conveyor system, match its features to the material, how much you move, the site, the distance, and how much is automated. Picking the right conveyor helps it work better, saves money, and makes things run smoother. This guide helps you use mining conveyor equipment in the best way for your mine.
- Common conveyor problems:
- Material falling off costs money and needs cleaning.
- Belt slipping uses more energy and costs more.
- Rough wear makes the conveyor work worse.
- Bad transfer spots make machines stop more.
- Matching issues make conveyor belts work less well.
Operational Needs
Picking the right mining conveyor system starts with knowing what your mine needs. You should check the ore type, how much you need to move, the site’s weather, and the land the conveyor will cross. Each thing changes how the conveyor works and how it is built. This guide helps you choose the best system for your goals.
Material Type
You must know what ore or bulk material you will move. The material’s features change which mining conveyor belt and system you pick. Different ores and bulk materials need special things:
- Abrasive ores need belts that do not wear out fast.
- Heavy ores need belts that are strong and do not break.
- Hot ores need belts that can stand high heat.
- Oily ores need belts that do not get ruined by oil.
- Hazardous ores need belts that do not catch fire and stop static.
If you match the belt system to the ore, you make it work better and fix it less. You also stop your work from stopping by surprise.
Throughput
Throughput means how much ore or bulk material you move in a set time. You need to know your goals and how much ore you want to move. Mining conveyor systems must move the right amount to keep work going.
- You can use throughput checks to split your conveyor into smaller parts.
- This lets you see if each part can move enough ore.
- Studies show this way is right over 90% when nothing blocks the system.
If you size your conveyor belt system for your needs, you stop slowdowns and keep ore moving. This helps you save money and make things better.
Site Environment
The weather at your mine changes which mining conveyor systems you pick. Heat and wetness can change how your conveyor belt system works. Look at the table below to see how different weather changes things:
| Environmental Factor | Impact on Conveyor Systems |
|---|---|
| High Temperatures | Belts wear out faster, more friction, belts break early, less grip, more energy used. |
| Low Temperatures | Materials break, belts tear, less bend, thick grease. |
| High Humidity | Metal rusts, mold grows on belts, wires fail. |
If your site is hot, you need belts that do not get ruined by heat and friction. Cold sites need belts that bend and do not tear. Wet sites need metal that does not rust and dry wires. If you match your conveyor belt system to your site, you keep work going and fix things less.
Distance & Terrain
You need to think about how far and what kind of ground you must move ore over. For long trips and rough land, overland mining conveyor systems are best. These systems move lots of ore and bulk material over hills, valleys, and bumpy ground. If your site has steep hills or goes up and down, you need a system made for that.
- Overland conveyors help move ore far away.
- They keep work going even when the land is hard.
- You move bulk material better and use fewer trucks or loaders.
If you match your conveyor system to the trip and land, you make it work better and spend less on moving ore. You also make your mine safer and easier to run.
Tip: Always check your site’s ore type, goals, weather, and land before you pick. This makes sure your mining conveyor system fits your needs now and helps you grow later.
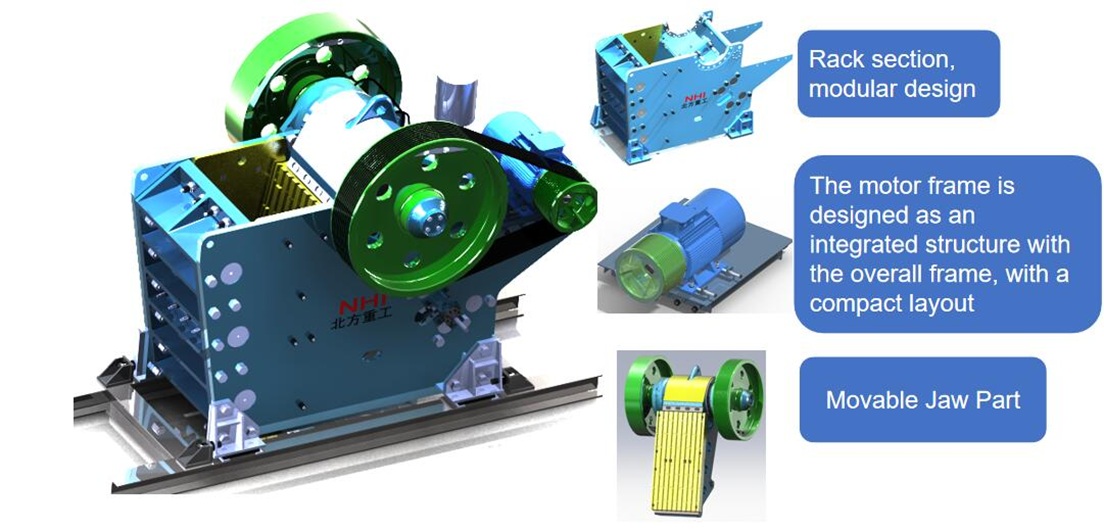
Mining Conveyor System Types

Picking the right mining conveyor system helps you work faster. It also helps you move ore and bulk materials better. There are many types of conveyor systems for mining jobs. Each system has special features for moving ore and bulk materials. They also help make production easier.
Belt Conveyor Systems
Belt conveyor systems are used most often in mining. They move ore and bulk materials over long distances. These systems can handle lots of material. They are simple and do not need much fixing. You can see their good and bad points in the table below:
Chain Conveyor Systems
Chain conveyor systems use metal chains linked together. They are strong and can carry heavy things. These systems are good for moving rough or heavy ore and bulk materials. Chain conveyors need oil and checks often. They work well with steel or wood pallets. They last longer than belt conveyors but need more care.
- Chain conveyors are strong and good for heavy loads.
- They need oil and checks to keep working.
- Belt conveyors are easier to fix but do not last as long with heavy use.
Screw Conveyor Systems
Screw conveyor systems use a turning screw to move ore and bulk materials. They work well on steep paths and help stop material from rolling back. These systems keep things from getting stuck. They are good for moving sand, cement, and other bulk solids.
Pipe Conveyor Systems
Pipe conveyor systems use closed pipes to move ore and bulk materials. They are good for fine powders and dusty solids. These systems keep dust and noise low. They also stop spills and make work safer. Pipe conveyor systems help keep work going and save money.
- The closed pipes keep dust and noise down.
- Stops spills, so work is faster and less waste.
- Can move fine powders and bulk solids.
Overland & Underground Systems
Overland conveyor systems move ore and bulk materials over hills and rough ground. They are good for moving things far away. Underground conveyor systems cost more to put in. They need special materials that do not catch fire and protect from dust. Underground systems can save money later because they use less energy and need less fixing.
- Underground conveyor systems cost more than overland ones.
- Overland conveyor systems move bulk materials over different land.
Tip: Pick your mining conveyor system based on what you need, the ore type, and your site’s weather and land. This helps you work better and get more done.
Key Selection Criteria
Safety & Compliance
Safety protection is the most important thing to check first. You need to keep workers safe and follow OSHA rules. Use guarding, emergency shut-off buttons, and warning systems. These things help stop accidents and keep ore moving. You also need regular maintenance and personal protective equipment. Sensors and alarms help you find problems fast. Stickers and warning labels remind workers about safety every day.
Here is a table that shows the main safety protection features and the OSHA rules:
You must check these safety protection features before using your mining conveyor belt. If you follow these rules, your site stays safe and you avoid fines.
Tip: Always train your team on safety and emergency steps. This keeps everyone ready and helps you meet the rules.
Maintenance Needs
You need to plan for maintenance when picking a mining conveyor system. Regular checks help you find problems early. Clean the conveyor belt system and look for wear. Oil moving parts and replace broken pieces. If you do maintenance, you stop breakdowns and keep ore moving. This saves money and keeps production on track.
Set a schedule for checking the conveyor belt system. Look at the belt, chains, screws, and pipes. Check sensors and alarms for safety. Fix small problems fast to avoid big repairs later. This keeps bulk material handling smooth and helps with optimization.
Note: Good maintenance keeps production high and stops delays in moving ore.
Budget & Cost-Effectiveness
You need to look at both the price to buy and the cost to run your mining conveyor system. The first cost is buying and installing the conveyor. The long-term cost is fixing, energy, and keeping it working. Balance these costs to get the best value.
If you spend more at first, you may save money later. A strong conveyor belt system needs less fixing and uses less energy. This keeps production high and makes moving ore cheaper. Check cost-effectiveness before you buy. This helps you plan for the future and keep your mine running.
Tip: Always compare the total cost of ownership, not just the price. This helps you make smart choices for your mining site.
Conveyor Belt System Features
Look at the features of each conveyor belt system before you choose. Some features help you move ore and bulk better. Others help you keep production high and stop breakdowns. Pick features that fit your needs and your site.
Here is a table that shows the top features for mining conveyor systems:
You can use sidewall cleated belt conveyors to keep bulk and ore from falling off. Advanced sensors give you real-time data to help with optimization. High-performance belt trackers help you avoid downtime and keep production moving. These features help you get the most from your mining conveyor system.
Tip: Pick features that help with bulk material handling, safety, and automation. This keeps production high and makes moving ore easy.
Technical & Custom Options
When you pick technical and custom options, you can make your mining conveyor system fit your needs. This helps you move more ore and bulk material. Custom choices can help your site work better and save money.
Drive Systems
Drive systems give power to your conveyor belt system. They are important for saving energy and keeping production steady. You can pick from different drive types for your mine. Gearless drives do not use gears, so they last longer and save energy. For example, the ABB drive at Bílina used 6–10% less energy than old drives. Gearless drives also need fewer motors, which saves more energy and money. If you pick the right drive, your conveyor system moves ore and bulk with fewer problems.
- Gearless drives last longer and use less energy.
- Fewer motors mean you save more energy.
- New drives help keep production steady and costs low.
Automation & Controls
Automation and controls help you run your mining conveyor system with less work. AI can find problems before they stop your conveyor. Digital twins let you watch your conveyor belt system as it works. Middleware connects your controllers, so you can move ore and bulk better. High-efficiency motors and VFDs help you control speed and save energy. Smart control systems find problems fast, so you keep moving ore and bulk.
Tip: Automation makes your conveyor belt system smarter and helps you stop delays.
Durability Upgrades
You can make your mining conveyor belt stronger for tough mining jobs. Different belts work best for different ore and bulk. Fabric belts bend easily and last a long time. Steel-cord belts are strong and good for long trips with heavy ore. Heat-resistant belts work with hot ore. Oil-resistant belts do not get ruined by oil. Fire-resistant belts are important for coal mining and keep things safe. Special belts can find rips and save energy, which helps move ore and bulk better.
If you pick the right upgrades, your conveyor belt system lasts longer. You keep production high and move ore and bulk without problems.